Highlights
- Security firm spotted an attack which exploits the ProxyServer vulnerability.
- The malware ProxyShellMiner uses the vulnerability to install crypto miners.
- ProxyShell vulnerability was tracked as CVE-2021-34523.

In a new malware discovery named ProxyShellMiner, the malware exploits the ProxyShell vulnerabilities to install cryptocurrency miners all around the Windows domain to make a profit for the threat actors.
For those who don’t know, ProxyShell is one of the Exchange Vulnerabilities found and fixed by Microsoft in 2021. Well, the three vulnerabilities are combined together; the vulnerabilities allow unauthorised, remote code execution and let the threat actors take full control of the Exchange server and turn to other parts of the enterprise server.
Now, the attacks were spotted by Morphisec and the threat actors abuse the ProxyShell vulnerability was tracked as CVE-2021-34523 to get the initial access to the organisation network
After that, the attackers deploy a NET malware payload into the NETLOGON folder of the domain controller to make sure that all the devices on the network are running on the malware.
Read: New Royal Trojan Variant Discovered, Targets VMware ESXi Virtual Machines
For the malware to activate, the malware requires a command line parameter which also works as a password for the XMRig miner component. ProxyShell uses an embedded directory, an XOR decryption algorithm and an XOR key which is downloaded from a remote server, mentioned Morphisec.
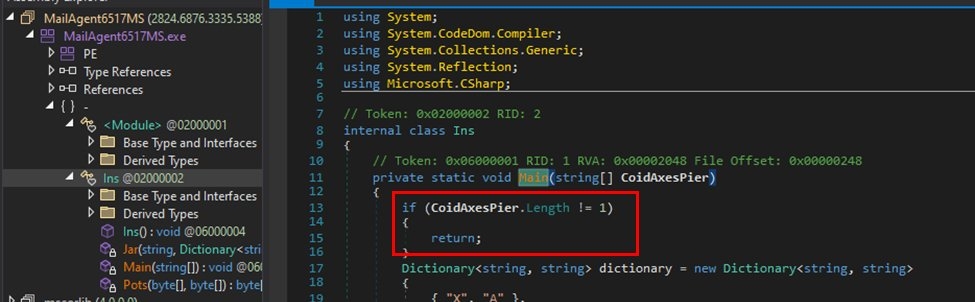
Furthermore, it uses a C# programme CSC.exe with “InMemory” compile parameters to execute the next embedded code modules. In the next phase, the malware downloads a file named “DC_DLL” and runs NET reflection to extract the argument for the task schedular, XML, and the XMRig key and then the DLL file is used for decryption of the additional files.
Read: Russian Threat Actors Target Cryptocurrency with Enigma Malware
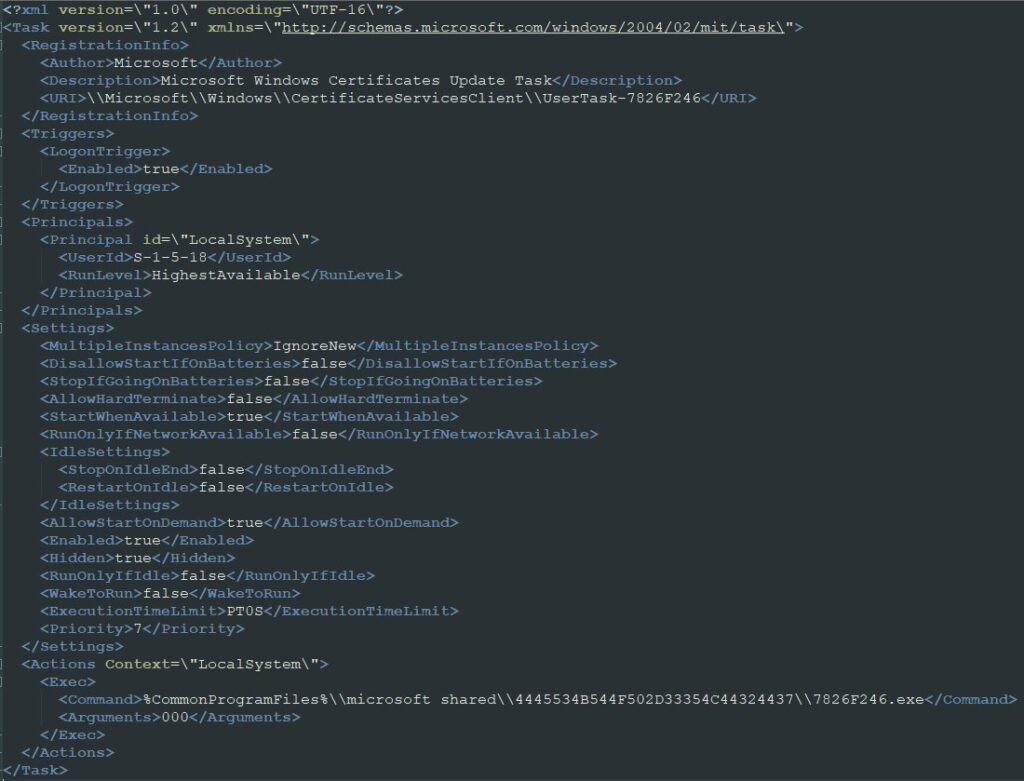
In addition to this, there’s a second downloader established connection on the compromised computer by creating a scheduled task which is configured on the user login. The Second downloader is downloaded from the remote location alongside the four other files.
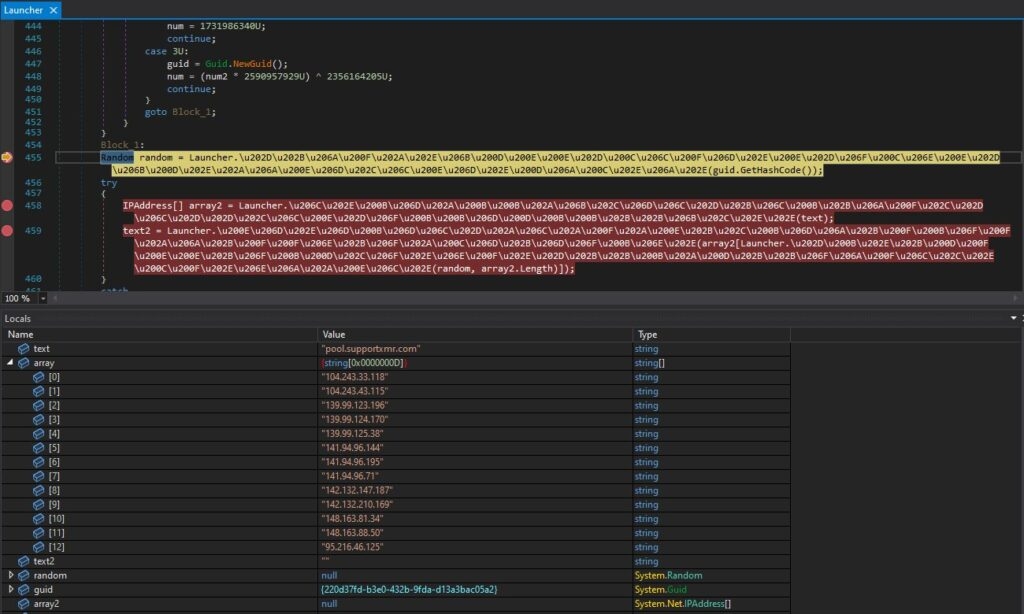
After all this, the file decides which browsers of the injected computer will be used for injecting the miner into the memory using a method known as “process hollowing” and then chooses a random pool from the hardcoded list, and the mining process begins.
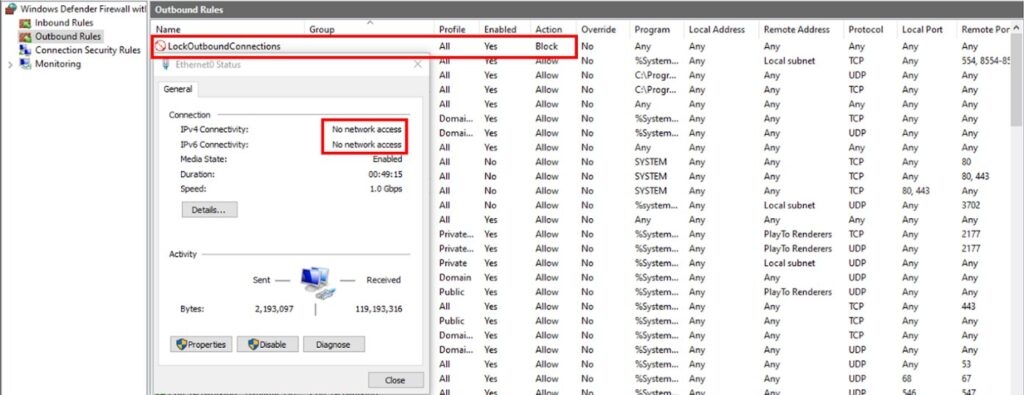
The last thing in this attack chain is to make a firewall rule that will block all the outgoing traffic which then applies to every Windows firewall and the reasoning behind doing this is to make the defenders less likely to detect malware & or get any notification about the possible injection from the breached system.
To escape the security programmes monitor the process runtime behaviour, and the malware waits for at least 30 seconds after the browser hollowing before making the firewall rule; it is quite possible that miners communicate with its mining tool through a backdoor that is not monitored by the security programme.
The security firms issues warning that the effect of the malware goes beyond just services outage and overheating the machines. As the threat actor gains a hold in the network and then the attackers can do anything from the backdoor deployment to executing a code.
Read: W4SP Stealer Found on PyPi Index, Threatening Crypto Wallets & Browser Passwords
Directly in Your Inbox









